blog categories
recent posts
blog tags

The transformer is essential component of the switching power supply. The commonly used magnetic cores of transformers are EE type cores, RM type cores, PQ type cores and EP type magnetic cores. How do these magnetic cores affect the transformer working? What are the advantages and disadvantages of each type core?
I. EE type core
It's easy to manufacture and assemble EE type cores. EE core has good heat dissipation and low cost, so it is the most widely used. But the disadvantage is that EE core can't provide self-shielding, therefore it is generally used in small and medium wattage power supplies.
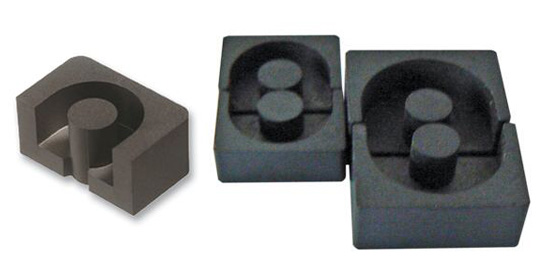
II. RM type core
The RM core has good heat dissipation and small volume. The volume of the RM core can be made smaller with the power supply, and the shielding effect is better than EE cores. Generally used in power supplies that require a small volume.
III. PQ type core
The design of the PQ core optimizes the ratio between core volume, surface area and winding area. The advantage of designing the PQ soft magnetic core is that it can provide the maximum inductance and the maximum winding area with the smallest core, and also make the magnetic circuit cross-sectional area of the core more uniform, so the core structure is better than other core structures. The design has fewer work hotspots.

IV. EP type core
The circular center column of the EP soft ferrite core has a three-dimensional structure. In addition to the end that is in contact with the PCB board, the winding is completely wrapped and the shielding is very good; this unique shape minimizes contact during assembly of the two cores. The effect of the air gap formed by the face and provides a larger ratio of volume and total space utilization.